Glossary
object
An object is the fundamental unit of content. Each object has a type and is stored in a database for that type. An object can be displayed as a link, as a small card, as a wide card, as an embed, or in a full page view (see views).
database
A database in Capacities is the fundamental storage unit for content. A database contains all objects of the same object type. So there is a database for all your images, another one for all your pages, another one for web links, and so on.
collection
A collection is a subset of a database and can therefore only contain objects of the same object type. It enables you to curate content of the same object type. An object can be part of as many collections as you like.
backlink
A traditional link is pointing from one content to another content and describes a unidirectional relationship. A backlink is a link that also shows up on the content that is being linked to, making it a bidirectional relationship.
Contextual backlinks include additional information to show the surrounding paragraph or other information around the place where the link has been made. You can read more in-depth thoughts about them here in Andy Matuschak's notes.
graph
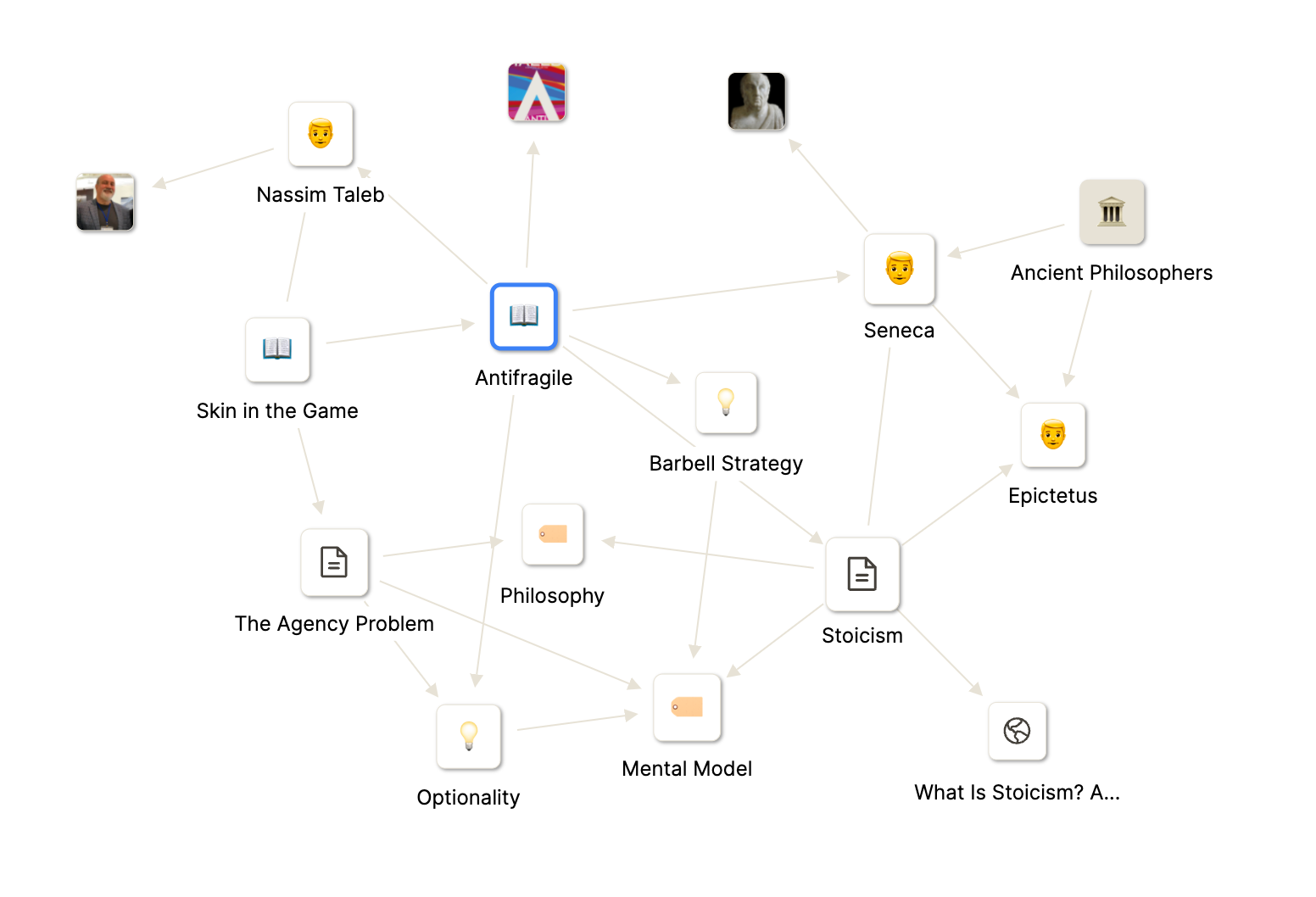
In Capacities, all notes are interconnected. They don’t have a fixed location. Every object is a node in a network and can be connected to others. And the most important thing: in Capacities, this happens by simply taking your notes. Mathematicians call these structures graphs
... which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph [...] is made up of vertices (also called nodes or points) which are connected by edges (also called links or lines). – From Graph Theory on Wikipedia
networked note-taking
Networked note-taking is the concept of highly connected notes – like a Wikipedia page. Your notes are not isolated but form a network and thus better reflect the way our brain works. The connections (explicit or implicit) help you to associate ideas, make sense of complex topic, and help you to build sustainable knowledge by attaching it to existing ideas.
object type
This is exactly the same as an object type. The terms are interchangeable, but we stick with object type now.
🤔 Do you find this explanation unclear or feel like something is missing in the docs?
With your help we can make the docs better for everyone. So just let us know, and we’ll improve it ASAP!
📨 Did reading the docs make you think of any product improvements?
Please let us know if you have an idea for a feature, think that something is missing or see a conceptual inconsistency that could be fixed. Just post it on our feedback board and discuss it with us and other users!
 Capacities Docs
Capacities Docs